What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)? Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, refers to a system where financial services are built…
Decentralized Finance: Unveiling its Influence on the Financial Landscape
admin
- May 10, 2024
5 min read

What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?

Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, refers to a system where financial services are built on blockchain technology, allowing for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for traditional intermediaries such as banks or financial institutions.
Why are Decentralized Finance Solutions Needed?
Understanding the necessity of DeFi Decentralized Finance solutions are needed to provide greater financial inclusivity, transparency, and accessibility to individuals worldwide. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, DeFi offers faster and more cost-effective financial services.
Why Are Useful? Decentralized Finance.
Exploring the benefits of DeFi solutions DeFi solutions offer numerous benefits, including decentralization, transparency, security, lower costs, and accessibility. These features empower individuals to have greater control over their finances and access to a wider range of financial services.
Types of Decentralized Finance Solutions Diverse applications within the DeFi ecosystem
1. Decentralized Exchanges (DEX): Online places to directly trade cryptocurrencies, keeping transactions private and secure without middlemen.
2. Decentralized Lending Platforms: Allow lending and borrowing of cryptocurrencies without banks, earning interest or accessing funds directly.
3. Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies tied to real assets, keeping their value steady for easy use on blockchain networks.
4. Decentralized Asset Management: Platforms for managing digital assets independently, without banks or brokers, for investing, trading, and diversifying.
5. Prediction Markets: Platforms where you can guess future event outcomes using cryptocurrencies, using collective knowledge for insights and risk management.
6. Insurance Platforms: Platforms for purchasing insurance with cryptocurrencies, using smart contracts to automate claims and make processes more efficient.
Features of Decentralized Finance Solutions Key characteristics defining DeFi platforms
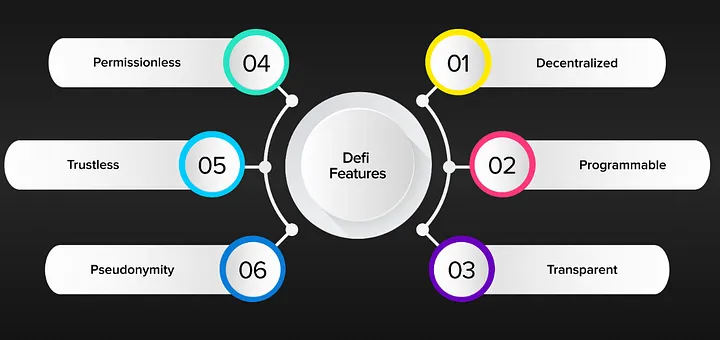
1. Decentralization: The distribution of control and decision-making across a network of participants rather than being centralized in a single authority or entity.
2. Transparency: The openness and clarity of information and processes within a system, allowing participants to easily verify and understand actions and transactions.
3. Security: Measures put in place to protect assets, data, and transactions from unauthorized access, fraud, or manipulation, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of the system.
4. Interoperability: The ability of different systems or networks to seamlessly communicate, share data, and operate together, promoting efficiency and compatibility across diverse platforms.
5. Programmability: The capability to execute automated actions or tasks through predefined instructions or code, enabling customization, flexibility, and innovation within the system.
6. Accessibility: The ease of access and usability of a system or service, ensuring that it is available and usable by all participants, regardless of geographic location, technical expertise, or socioeconomic status.
Supercharge your startup with our FREE MVP Guide E-Book
Download it now to kickstart your growth and turn your ideas into reality.
Benefits of Decentralized Finance Solutions Advantages of embracing DeFi in financial operations
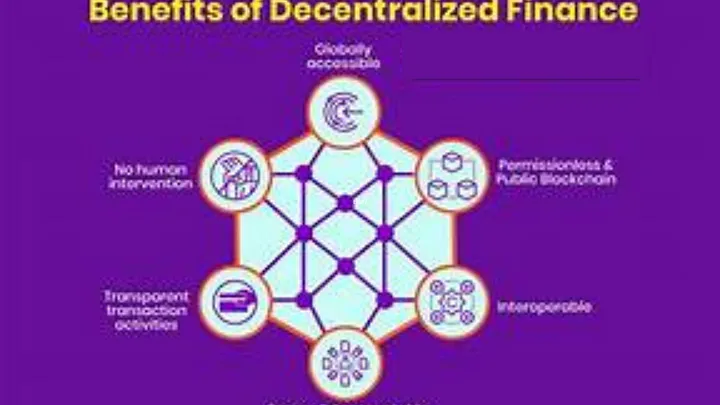
1. Lower transaction costs: Reduced fees for financial transactions, making participation more affordable.
2. Increased financial inclusivity: Expanded access to financial services for underserved populations, fostering economic growth.
3. Enhanced security and transparency: Improved protection of data and transactions, fostering trust among participants.
4. Improved access to liquidity: Greater availability of funds for trading, lending, or borrowing, enhancing financial operations.
5. Global accessibility: Access to financial services worldwide, promoting inclusion across borders.
6. Automated and efficient processes: Use of technology like smart contracts to streamline transactions, increasing efficiency.
Utilization Cases of Decentralized Finance Solutions Real-world applications of DeFi across various sectors

1. Remittances and cross-border payments: Sending money across borders to family and friends.
2. Peer-to-peer lending: Direct lending and borrowing between individuals.
3. Tokenization of assets: Converting real-world assets into digital tokens for easier ownership transfer.
4. Decentralized trading: Trading digital assets directly between users.
5. Insurance and risk management: Providing insurance coverage and managing risks using smart contracts.
6. Decentralized finance for underserved populations: Offering financial services to those lacking traditional banking access.
Utilized Technologies in Decentralized Finance Technological foundations enabling DeFi innovation
1. Blockchain
2. Smart contracts
3. Decentralized storage solutions
4. Oracles
5. Interoperability protocols
6. Decentralized identity systems
The Future of Decentralized Finance.

Predictions and trends shaping the future of DeFi The future of DeFi holds promises of continued growth, innovation, and mainstream adoption. Emerging trends include the integration of DeFi with traditional finance, scalability solutions, and regulatory developments.
How can Arowiz Technologies help with Decentralized Finance?
Utilize Arowiz Technologies for seamless DeFi integration and development. Our expertise in blockchain and DeFi solutions ensures tailored solutions for businesses. With over 12 years of experience, we’ve delivered 100+ successful projects, helping startups achieve significant funding.
Supercharge your startup with our FREE MVP Guide E-Book
Download it now to kickstart your growth and turn your ideas into reality.
FAQ
Q1. What is the difference between DeFi and traditional finance?
Traditional finance relies on centralized institutions like banks and governments, while DeFi operates on decentralized blockchain networks, removing intermediaries for peer-to-peer transactions.
Q2. How secure are DeFi platforms?
DeFi platforms use blockchain technology, inherently secure due to decentralization. However, vulnerabilities like smart contract bugs exist, so users must research and use trusted platforms.
Q3. Can anyone participate in DeFi?
Yes, anyone with internet access and a compatible device can participate in DeFi through decentralized applications offering financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading.
Q4. What are the risks associated with DeFi investments?
Risks include smart contract vulnerabilities, market volatility, regulatory uncertainties, and potential loss due to hacking or fraud. Investors should conduct research and invest cautiously.
Q5. How do decentralized exchanges work?
DEXs enable peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading without intermediaries. They operate on blockchain networks, using smart contracts for automated trading while users maintain control of their funds.
Conclusion
Summarizing the impact of DeFi on the financial landscape and the potential it holds for the future. DeFi is revolutionizing the way financial services are accessed and delivered, offering greater inclusivity, efficiency, and security. As businesses and individuals embrace decentralized finance, the possibilities for innovation and growth are limitless.
Pro Tip — Prioritize thorough research before investment. Secure private keys, diversify portfolios, and monitor regulatory updates for successful implementation.
Join our free newsletter for more insights — click the link below
Subscribe to our Newsletter: https://lnkd.in/dYmBdX3c
Visit Our Blog: https://arowiz.com/blog/
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://lnkd.in/d4KZJakS.
Tags
- BlockchainDefiFinanceLandscapesoftware development
Our New Letter
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
Ready for more?

Arowiz Technologies is a Central India-based customer Centric software development & Expert IT Staff Augmentation company ...
FOR JOBS
hr@arowiz.comFOR SALES
sales@arowiz.comMARKETING / BLOGS
info@arowiz.comGET CONNECTED
Top Industry
About Us
Top Services
Hire Expert Developers
- AI / ML Developers
- Blockchain Developers
- DevOps Developers
- Web3 / Gaming Developers
- Full Stack Developers
- AR / VR – Meta Developers
- Python Developers
- Solidity Developers
- Node.js Developers
- ReatJs Developers
- Next.Js Developers
- Flutter Developers
- React Native Developers
- Golang Developers
- Mobile App Developers








